|
Celebrating 34 years providing high quality products and advice.
|
| Our Local Time Is 4:19:20 AM. |
| Call us at 818-786-0600. We are here to help! |
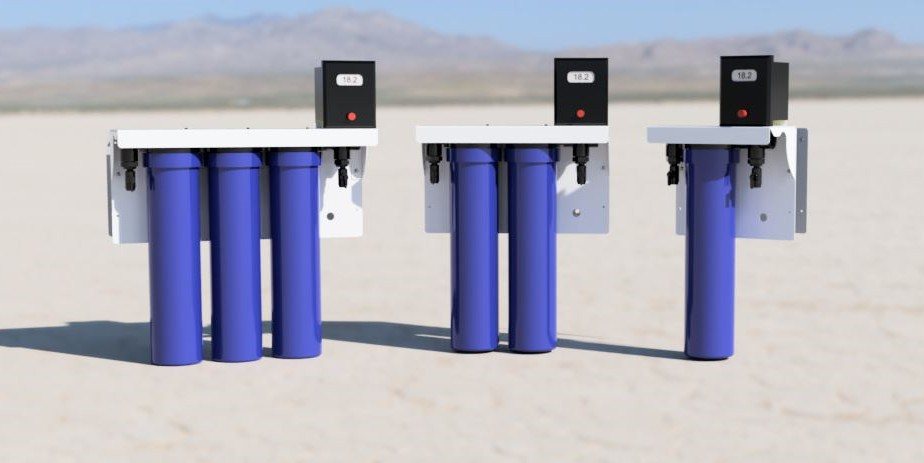 |
ON SALE NOW
Introducing the Polaris Lab Water Systems
High Purity Water Made In The USA.
Click here for more info. |
Laboratory Water Purification Technologies
Water purification is a step-by-step process often requiring a combination of technologies. Barnstead is the only manufacturer of a complete range of equipment utilizing all technologies necessary to purify water in your laboratory.
Also See :
Laboratory Water Specifications
Common Lab Water Impurities
Distillation
Distillation is the most common water purification technology in laboratories worldwide. Water undergoes phase changes during the process, changing from liquid to vapor and back to liquid. It is the change from liquid to vapor that separates water from the dissolved impurities. Distillation has the broadest capabilities of any single form of water purification.
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis occurs when water is pushed through a semipermeable membrane using external pressure. The membrane has molecular weight cut off in the 300 Dalton range. Most water impurities do not pass through the membrane. They collect on the membrane surface and are flushed to the drain. Reverse osmosis is a popular method of pretreatment to distillation or deionization systems and for purifying water for general applications such as glassware and plasticware washing.
Deionization
Deionization is also referred to as demineralization or ion exchange. It is the removal of ions from feed water by synthetic resins. These resins have an affinity for dissolved inorganics and are divided into two classifications: cation removal resins and anion removal resins. Deionization is the only technology which produces the resistivity requirement for Type I reagent grade water.
Filtration:
Particulate Filtration
Depth filters are commonly made by winding fiber around a hollow and slotted tube. As water passes through the fiber toward the tube, particles are removed and held in the fiber. Depth filtration is used as a first step in most water purification systems to remove particulate matter. Membrane filters usually have a submicron pore size.
Particles and bacteria cannot pass through the membrane and are held on the membrane surface. Membrane filtration includes reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration. It is also used as a final step in deionization systems to prevent submicron particles and bacteria from entering the product water.
Ultrafiltration (UF)
Ultrafiltration is used in reagent grade water systems primarily to remove pyrogens (bacterial endotoxins) from water. The ultrafiltration membrane has a molecular weight cut off of less than 10,000 Daltons. Pure water permeates the membrane but particles, pyrogens, colloidal silica, bacteria, and high molecular weight organics are rejected.
Adsorption
Adsorption uses high surface area activated carbon to remove organics and chlorine from feed water. It is used as a first or second step in most water purification systems and may be used as a final step to achieve low TOC. Organics and chlorine adhere to the surface of the activated
carbon and remain in the cartridge.
Ultraviolet (UV) oxidation
Photochemical oxidation with ultraviolet light at dual, 185 and 254, nanometer wavelengths can eliminate trace organics, and kills microbes in pure water. When used in a Barnstead reagent grade water system, ultraviolet light can reduce trace organics to less than 1 ppb TOC. Ultraviolet ight at a 254 nanometer wavelength can be used in storage reservoirs or distribution lines to prevent bacterial growth.
Combination Ultraviolet oxidation and Ultrafiltration (UV/UF)
The use of ultraviolet oxidation and ultrafiltration technologies in conjunction with adsorption and deionization in the same system produces water free of virtually all impurities. These technologies have demonstrated the ability to remove nucleases such as RNase, DNase and DNA when challenged with known concentrations of the material. The UV/UF units produce reagent grade water with resistivities up to 18.3 megohm-cm, organics < 2 ppb, pyrogens <0.001 EU/ml and no detectable RNase, DNase or DNA.
Source - Barnstead Basic Water
|
Images are representative of the products. Images may or may not be of the actual product. If it is important e-mail us for an actual image if available.
* Flat Rate UPS shipping when able to ship via UPS and is in the USA excluding Hawaii and Alaska.
Larger Items may not be able to ship via UPS, in that case freight charges will be quoted seperately.
International shipping will be quoted after the order is placed. You will have the opportunity to cancel before we finalize your order.
Terms and conditions
Credit Application
Privacy
Policy
List All Products
|